Rules, Policies, and Design Considerations for Rainwater Harvesting in Factory Buildings
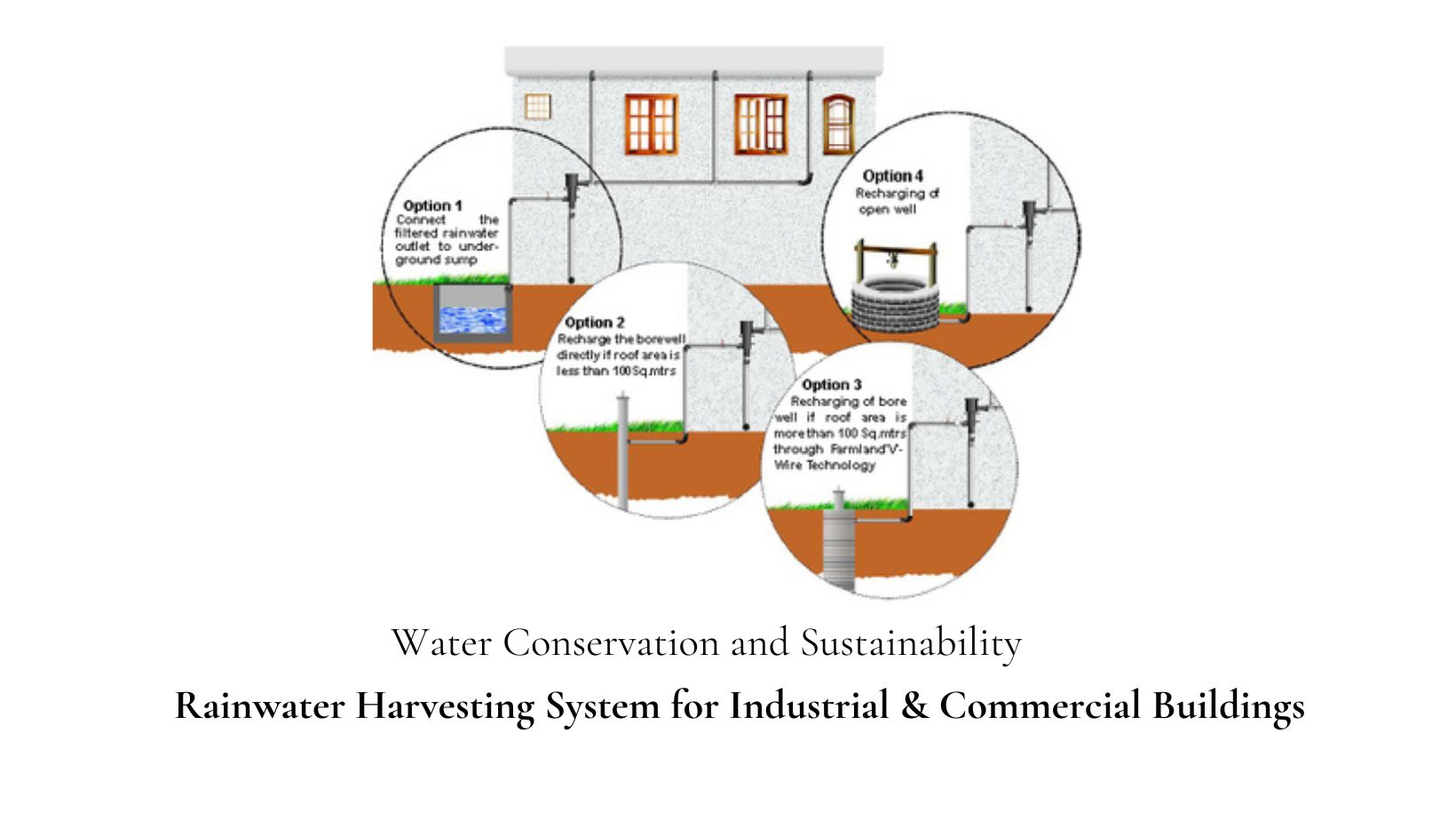
Water scarcity is a pressing global issue, and India, in particular, faces significant challenges in water management. Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is a sustainable solution that can contribute to water conservation efforts, particularly in industrial settings. Implementing RWH systems in factory buildings not only helps in meeting water requirements but also contributes to groundwater recharge. This article aims to provide insights into the rules, policies, and design considerations for rainwater harvesting project implementation in a factory building.
Understanding Rules and Policies
a. Familiarize yourself with local regulations: Before initiating any rainwater harvesting project, it is crucial to understand the rules and policies specific to the region where the factory building is located. Different states in India may have varying guidelines, permits, and incentives related to RWH.
- The National Building Code (NBC): The NBC has provisions for rainwater harvesting in buildings, and factory buildings are no exception. Compliance with the NBC ensures that the rainwater harvesting system meets the required standards.
- State-Specific Regulations: Different states in India may have their own rules and guidelines related to water management and rainwater harvesting. It is essential to be aware of and adhere to these state-specific policies.
- Industrial Regulations: The factory may have industry-specific regulations that must be considered while designing and implementing rainwater harvesting systems.
b. Consult with relevant authorities: Engage with local water resource departments or municipal corporations to ensure compliance with regulations. Obtain the necessary approvals, permits, and clearances before commencing the project.
c. Incorporate national guidelines: Refer to the “Model Guidelines for Rainwater Harvesting” issued by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA), Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India. These guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for rainwater harvesting systems and can help in the design and implementation process.
Design Considerations for Rainwater Harvesting
a. Assess rooftop suitability: Evaluate the rooftop area of the factory building for rainwater harvesting potential. Consider factors such as size, structural integrity, material, and slope. Ensure that the roof surface is free from debris, vegetation, or any other contaminants that may affect water quality. Additionally, the roofing material should be non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals that could contaminate the collected rainwater.
- Optimize catchment area: The size of the catchment area (i.e., rooftop) should be proportional to the water demand and the anticipated rainfall. Calculate the maximum potential rainwater yield using historical rainfall data and the catchment area.
- Gutter System: Properly designed and maintained gutter systems are essential for effectively channeling rainwater from the roof to the storage or recharge system. Regular cleaning of gutters and downpipes is vital to prevent clogs and blockages.
- Determine storage capacity: Based on water requirements, design an appropriate storage system. Consider factors such as average daily consumption, number of employees, and the availability of alternate water sources during dry periods. Adequate storage capacity ensures a continuous supply of water, even during extended periods without rainfall.
- Filter and treatment mechanisms: Install effective filtration systems to remove debris, sediment, and pollutants from harvested rainwater. Depending on water quality, additional treatment methods like disinfection or purification may be required. The treated water should meet the quality standards set by local health authorities.
- Overflow and recharge system: Include overflow provisions to prevent waterlogging or damage to the building. Design a system that allows excess rainwater to be directed towards recharge structures, such as recharge pits or borewells, to replenish the groundwater table. If the factory is located in an area with declining groundwater levels, groundwater recharge through rainwater harvesting can be beneficial.
- Safety Measures: Ensure that the rainwater harvesting system does not compromise the structural integrity of the factory building. Safety measures should be implemented to prevent accidents or mishaps during installation and maintenance.
Implementation and Maintenance
- Engage professionals: Collaborate with experienced rainwater harvesting consultants or experts who specialize in designing and implementing such systems. Their expertise ensures optimal utilization of resources and adherence to quality standards.
- Regular maintenance: Schedule periodic inspections to check the efficiency of the system, including filters, pumps, storage tanks, and recharge structures. Clean filters and tanks as needed, and ensure that all components are in good working condition.
- Awareness and training: Educate factory employees about the importance of rainwater harvesting, the benefits, and the role they can play in maintaining the system. Conduct training programs to ensure everyone understands their responsibilities and practices water conservation.
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting in factory buildings offers a practical and sustainable solution for meeting water demands while contributing to groundwater recharge. By adhering to local rules, and policies, and considering the design and implementation guidelines outlined in this article, factories can establish efficient rainwater harvesting systems. These systems not only enhance water management practices but also contribute to environmental sustainability, promoting a greener and more water-secure future for India.

