Digital Earth Fault Relay: Enhancing Electrical Safety with Precision Technology
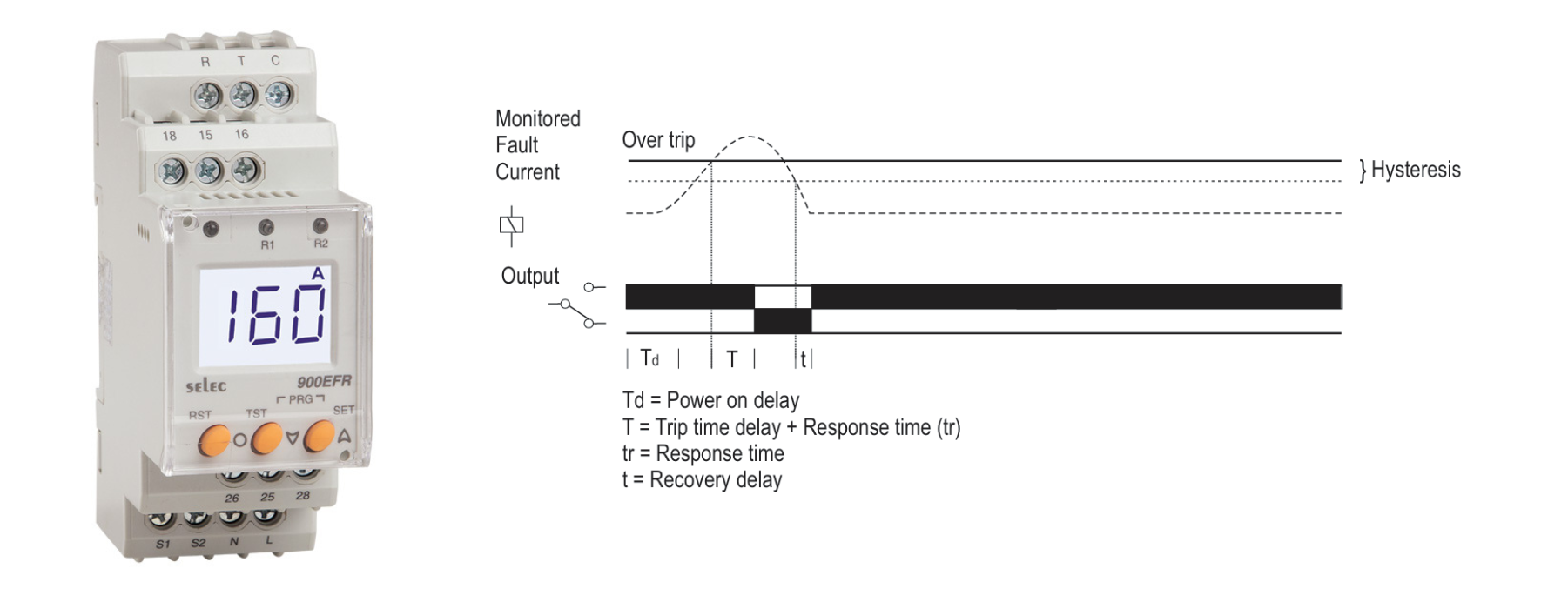
The world of electrical safety has witnessed significant technological advancements in recent years, and one such innovation at the forefront is the Digital Earth Fault Relay (EFR). This device, often underappreciated, plays a crucial role in safeguarding both people and equipment from electrical faults that can cause fires, electrical shocks, and severe damage to electrical systems. While the traditional electromechanical earth fault relays have served the industry for decades, digital versions have introduced new levels of precision, reliability, and features that are often unknown to many. In this article, we’ll explore the latest developments, applications, and benefits of Digital Earth Fault Relays, along with a look at a few leading brands in India…
What is a Digital Earth Fault Relay?
A Digital Earth Fault Relay (EFR) is an advanced protection device used to detect and isolate earth faults in an electrical system. Unlike traditional relays that rely on mechanical movement or analog circuitry, digital relays leverage microprocessor technology to provide faster, more accurate responses and additional functionalities.
How does it work? The relay monitors current imbalance in a system. When an earth fault occurs (e.g., when a live conductor touches an earthed surface or when there is insulation failure), the relay detects the fault current, processes the data digitally, and initiates a trip signal to disconnect the faulty section of the circuit. This quick intervention prevents further damage, ensures safety, and minimizes downtime.
Why Use Earth Fault Relays in Industrial Factories?
Industrial factories operate with high-power equipment and complex electrical networks that are prone to faults. Earth faults can occur due to insulation failures, equipment aging, or environmental conditions like moisture and dust. These faults, if undetected, can lead to devastating consequences such as:
- Equipment Damage: Fault currents can damage expensive machinery, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
- Fire Hazards: Prolonged earth faults can generate heat, potentially causing electrical fires.
- Safety Risks: Workers are exposed to electric shock hazards, which can lead to severe injury or even death.
- Downtime: Undetected faults can disrupt operations, leading to production losses and inefficiency.
Using earth fault relays ensures that any fault in the electrical network is quickly detected and isolated, minimizing the risk of accidents, equipment failure, and costly downtime.
Where Should Earth Fault Relays be Used in Industrial Factories?
In an industrial setup, earth fault relays should be installed in key areas where earth faults are likely to occur or where the consequences of such faults would be most critical. These include:
- Switchgear Panels: Install relays in the main switchgear and distribution panels to monitor the overall health of the electrical system.
- Transformers: Earth fault relays provide crucial protection in transformer circuits, preventing transformer winding damage due to ground faults.
- Motor Control Centers (MCCs): Motors are prone to insulation failure, and earth faults here can disrupt industrial processes. Relays can detect faults early and isolate them, preventing further damage.
- Substations: In substations, earth fault relays provide protection against ground faults in high voltage and medium voltage systems, ensuring the continuity of power distribution.
- Power Generators: Generators are often the backbone of industrial power systems. Earth fault relays protect generators from damage caused by earth faults in generator windings or associated circuits.
- Cable Networks: Underground or overhead power cables are susceptible to earth faults due to environmental factors. Earth fault relays installed in cable distribution systems help in early fault detection.
How to Use Earth Fault Relays in Industrial Factories
- Assess the Electrical Network: Before installing earth fault relays, conduct a thorough assessment of the electrical network to identify the critical areas where faults are likely to occur.
- Select the Appropriate Relay Type: Depending on the system voltage, current, and fault sensitivity requirements, choose the right type of digital earth fault relay. Ensure that the relay has the right protection features for your specific applications, such as adjustable sensitivity, multiple protection functions, and communication capabilities.
- Coordinate with Existing Protection Devices: Ensure that the earth fault relay is correctly coordinated with other protection devices such as circuit breakers and overcurrent relays to avoid unwanted tripping and ensure selective fault isolation.
- Set Fault Detection Sensitivity: Adjust the relay’s sensitivity to detect earth faults at the desired threshold. Set it at a level that ensures early detection without causing nuisance trips.
- Integrate with Monitoring Systems: Connect the relay to centralized monitoring systems so that real-time data on system health and fault occurrences can be tracked. This helps in diagnosing problems quickly and efficiently.
- Test and Commission the System: After installation, perform a thorough test of the system to ensure that the relay functions as expected. This includes simulating earth faults and checking the relay’s response time and fault isolation.
Cautions Electrical Maintenance Managers Must Take
- Regular Maintenance and Testing: Digital Earth Fault Relays, like any other electronic device, must be periodically tested and maintained. Conduct periodic testing to ensure that the relay functions correctly, and calibrate the system if necessary.
- Coordination with Protection Devices: It’s crucial to ensure that the earth fault relay is properly coordinated with other protection devices, such as overcurrent relays or circuit breakers. Improper coordination can result in mis-tripping or failure to isolate the fault.
- Avoid Over-Sensitivity: Setting the relay to be overly sensitive can lead to nuisance tripping, causing unnecessary downtime. Ensure that the sensitivity is balanced to detect actual faults without tripping due to minor fluctuations.
- Data Monitoring and Analysis: Regularly monitor the data from digital relays to detect any abnormalities in the system. The data logged by these relays provides insights into the system’s condition, and any repeated fault occurrences must be analyzed for underlying issues.
- Environmental Considerations: Ensure that relays are installed in areas protected from dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures, as these conditions can affect their performance. Use enclosures or proper insulation to protect relays in harsh environments.
- Training for Staff: Ensure that the maintenance staff is well-trained in the use of digital relays. They should be able to interpret fault data, adjust settings as required, and conduct necessary maintenance.
- Documentation and Compliance: Always ensure that relay settings and testing procedures are documented. This helps in ensuring compliance with safety standards and simplifies troubleshooting and future maintenance.
Benefits of Digital Earth Fault Relays
- High Accuracy and Reliability: The microprocessor-based technology in digital relays improves fault detection accuracy, helping prevent major system failures.
- Reduced Maintenance and Downtime: With self-diagnostic features and fast fault isolation, digital relays reduce manual inspections and minimize system downtime.
- Cost Savings: Though initially more expensive, digital relays’ lower power consumption, reduced maintenance, and extended equipment life provide substantial cost benefits over time.
- Improved Safety: By detecting faults faster and more accurately, digital relays help prevent electrical fires and reduce the risk of electrical shocks.
Unique Features of EFRs
While Digital Earth Fault Relays are known for their reliability and precision, there are several new features and capabilities that make them particularly beneficial in modern electrical systems:
- Customizable Sensitivity: Digital relays allow fine-tuning of fault detection sensitivity. This capability enables the detection of even low-level earth faults that could be missed by conventional relays, preventing larger system issues.
- Self-Diagnosis and Communication: Equipped with self-diagnosis capabilities, digital relays can monitor their own health and performance. Some advanced models even communicate with centralized monitoring systems, providing real-time data on faults and relay performance, facilitating proactive maintenance.
- Multi-Functional Protection: In addition to earth fault detection, many modern digital relays offer overcurrent, phase imbalance, and short circuit protection, providing comprehensive safety in a single unit.
- Event Logging and Data Storage: Digital relays can log fault events, including the date, time, and fault magnitude. This data can be analyzed post-event to diagnose system issues and prevent recurrence.
- Remote Monitoring and Operation: With IoT integration, digital relays allow for remote monitoring and control. This feature is especially valuable in industrial plants, where quick response to faults can significantly reduce downtime.
- Energy Efficiency: Digital relays consume less power compared to electromechanical models, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
Leading Brands in India
India’s growing industrial and commercial sectors require robust electrical protection systems, and several prominent brands provide high-quality Digital Earth Fault Relays:
- L&T (Larsen & Toubro): L&T offers a wide range of digital protection devices, including earth fault relays, known for their durability and advanced features suitable for various industries.
- Schneider Electric: Schneider’s digital relays are renowned for their precision and integration with smart grids, making them popular in utility and industrial applications.
- Siemens: Siemens provides a comprehensive range of protection relays that offer multi-functionality, making them suitable for large-scale industrial applications in India.
- ABB: ABB’s protection relays are designed with a focus on innovation, offering features like remote operation and advanced fault analysis, ideal for critical infrastructure projects.
- Havells: A trusted name in electrical solutions, Havells offers earth fault relays that cater to small and medium-sized industries, focusing on energy efficiency and safety.
- Selec: Selec, an Indian brand known for its cost-effective and reliable products, offers digital earth fault relays that cater to industries seeking robust protection solutions at competitive prices. Their relays come equipped with features like adjustable trip settings, making them versatile for various electrical installations.
- Elmeasure: Another key player in the Indian market, Elmeasure specializes in energy management systems and protection devices. Their digital earth fault relays are designed to integrate seamlessly with energy management solutions, providing users with enhanced fault detection, monitoring, and energy-saving capabilities.
Conclusion
The evolution of the Digital Earth Fault Relay is a testament to the advancements in electrical safety technology. These devices offer significant improvements in fault detection, energy efficiency, and reliability compared to traditional electromechanical models. With features like customizable sensitivity, remote monitoring, and data logging, digital earth fault relays are indispensable in modern electrical protection systems across industries.
As industries increasingly adopt digital relays, the Digital Earth Fault Relay will continue to play a pivotal role in safeguarding electrical systems, reducing operational costs, and preventing catastrophic failures. The future of electrical safety lies in embracing these advanced technologies, making them a smart investment for businesses and utilities alike.

